Preventing Medical Errors with Better Communication
Poor communication is a major factor in medical negligence and, in one study of patients, 60% experienced errors due to communication failures. Clear lines of communication between healthcare professionals, patients and their families are essential for good quality, continuous care in hospitals. In some cases, alternative forms of communication such as sign language or observing body language are necessary, and it is important that staff take the time to interact sufficiently with non-verbal patients to provide effective care. Without accurately passing on medical information and listening to patient’s concerns, errors leading to medical negligence and patient injury can occur at any stage of treatment. A diagnosis based on incorrect data, a prescription for the wrong medication, or a healthcare team’s failure to share information during a difficult birth can all lead to preventable injuries.
Improving Communication During Childbirth
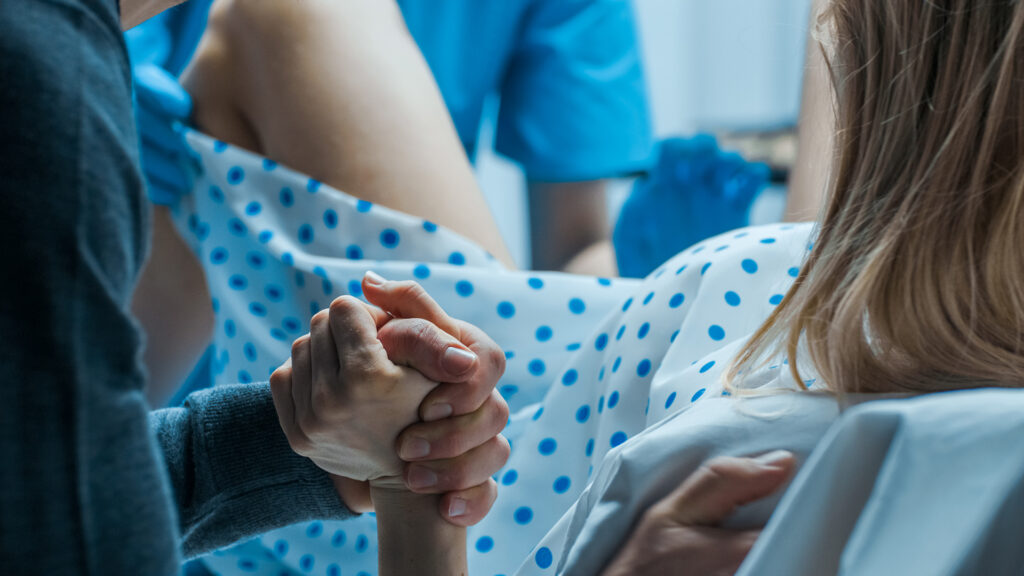

While childbirth always carries a risk of injury to both mother and baby, it is estimated that almost a third of birth injuries are preventable. A common cause of unnecessary injuries is a lack of communication during the delivery process, both between the OBGYN and mother and within the healthcare team responsible for the birth. Without good communication and continuity of care, this can lead to OBGYN negligence where a doctor fails to properly monitor progress of the delivery and administer treatment if necessary. By clearly outlining roles for each medical professional, regularly sharing updates on the patient’s status, and listening to the mother’s concerns, the risk of injury can be reduced. According to JJS Justice, legal experts in the medical negligence field, most obgyn negligence cases involve obstetricians who failed to adequately monitor the mother or the fetus. A lack of communication feeds this negligence.
Communication Strategies at Consultation
Poor communication between healthcare professionals and their patients during a first consultation can also have an impact on patient safety throughout the rest of their treatment. Patients may misunderstand a doctor’s diagnosis, the instructions for booking further tests or how to take their prescribed medication. In extreme cases, a patient may give their consent to a medical procedure without being properly informed of its consequences, which could result in a case for medical malpractice. To address these issues, there are several communication strategies in healthcare that can help to improve patient safety. When staff are taught models such as RELATE (reassure, explain, listen, answer questions, take action and express appreciation), they become more aware of each stage of a consultation and will take steps to ensure that each has been adequately carried out and understood by the patient.
Supporting Patients with Impaired Communication

Misunderstandings can also arise when clinicians are dealing with anyone who has issues with communication. This could be because of a physical impairment such as deafness or a developmental disorder like Alzheimers. As a result, people with disabilities that affect their understanding or communication skills can be more at risk of medical errors as they are less able to explain their symptoms and ask questions about their treatment. Taking the time to read a patient’s body language, use sign language or write down simple instructions on a piece of paper can all improve interaction with non-verbal patients.
Overcoming Language Barriers
Other challenges to communication include language barriers which can lead to poorer quality healthcare. Patients with limited English proficiency (LEP) tend to remain longer in hospital and have a 25% higher risk of readmission to hospital within 30 days than English speaking patients. Large healthcare institutions that deal with many different language groups are likely to have their own interpreting services and access to resources for better communication. In smaller clinics that are still seeing greater diversity in their intake, providing the equipment for telephone or video interpretation can significantly improve a patient’s access to healthcare and overall satisfaction with their treatment.
Digital Tools To Improve Quality of Patient Care

As well as having access to technology for the purpose of interpretation, almost 84% of hospital decision-makers believe digital tools could improve quality of care. Delays in accessing records, receiving lab reports and sharing patient data could be minimized with the greater use of digital communication platforms. By providing healthcare workers with their own personal devices, and the appropriate software that will enable them to exchange essential information quickly and without confusion, medical mistakes caused by a breakdown of communication can be avoided.
Ensuring Continuity of Care at Handoffs
Errors in patient care often occur as a result of poor communication during transition of care or hand-offs. This is when a patient is transferred to another healthcare provider or simply continues their treatment with a different team of nurses after a shift change. The potential for essential information transmitted at this stage to be inaccurate, misinterpreted or omitted is very high, especially in a busy hospital. The quality of handoffs can be improved through more thorough team training and with the implementation of tools such as forms and checklists. By implementing a handoff improvement program, a number of medical centers have managed to successfully reduce the occurrence of avoidable adverse events by almost a third.
Avoiding Medication Errors After Discharge

One important transition of care is leaving a healthcare setting altogether and, every year, hospitals deal with more than 35 million discharges from hospitals. One study revealed that, of a group of patients treated for acute coronary syndrome or heart failure, over 50% experienced errors with their medication within a month of their discharge from hospital. Mistakes with medication often lead to readmission to hospital as they can cause a new condition or lead to severe injury in patients. As well as checking a patient’s list of medication is accurate and up-to-date, errors can be reduced through more effective communication both with the patient and their caregivers, who are often responsible for administering their medication. This will help to ensure not only that the medication is correct but that the patient takes the right dose at the right time.
Medical errors are common and can often lead to preventable injury in patients. By improving channels of communication within healthcare teams, between doctors and patients and during transitions of care, mistakes can be avoided and the health and safety of patients maintained.




