The Future of Neurosurgery: Advancements in Brain Imaging and Surgical Techniques

Are you wondering how neurosurgery will advance in the upcoming years?
The field of neurosurgery is rapidly advancing, and new imaging techniques and surgical procedures are being developed. This article explores the future of Neurosurgery and discusses the exciting advancements that are currently taking place.
The advances being made in brain imaging
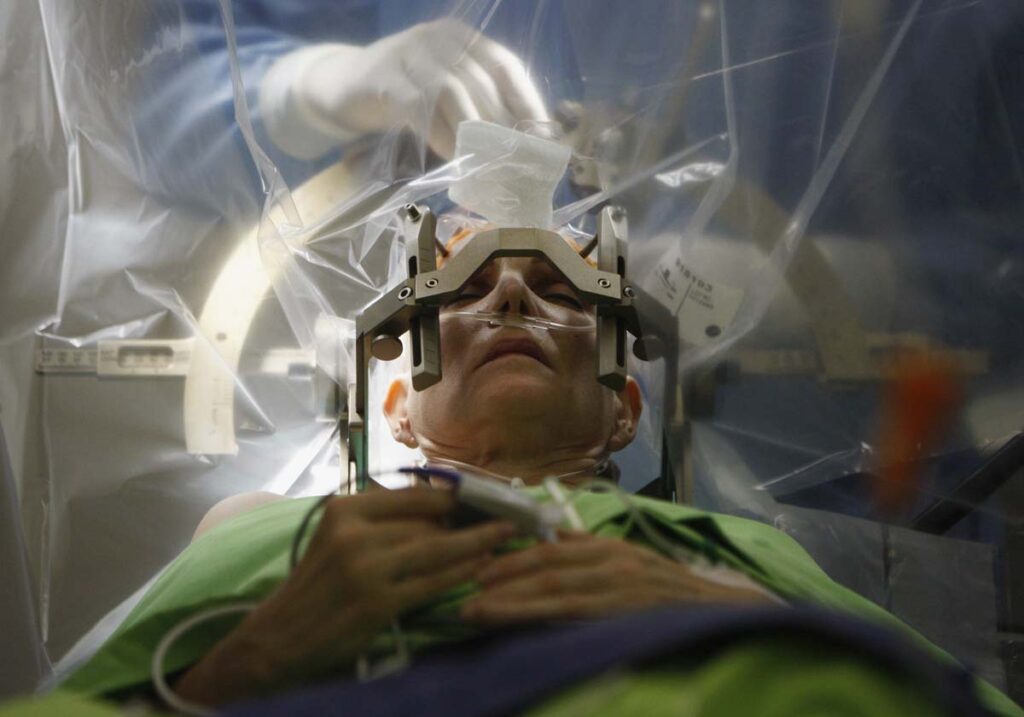
The advances being made in brain imaging are allowing neurosurgeons to diagnose and treat neurological disorders with greater precision and accuracy than ever before. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scans and others are now essential tools used by neurosurgeons in Austin to provide detailed pictures of specific areas of a patient’s brain. This detailed imaging allows neurosurgeons to map out the area they will be operating on in minute detail, a task that was previously done using paper-based measurements.
The use of enhanced imaging technologies, such as functional MRI (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), is changing how certain neurological conditions are treated. These techniques enable the direct visualization of how various structures in the brain interact with one another, providing surgeons with direct guidance during the operation process and allowing them to target the specific area of surgery for maximum effect with minimal risk.
The growth in technologies such as 3D printing is also having an impact on how surgeons plan complex operations that involve intricate anatomical details or require unique instrumentation for placement. Furthering this development are robotic surgical systems, which are used increasingly for minimally invasive procedures due to their ability to provide highly accurate incisions or even implant medical devices within delicate tissues or organs. With these advancements, we can expect more sophisticated procedures in the near future that will help improve the lives of those who suffer from severe neurological disorders.
The advances being made in surgical techniques
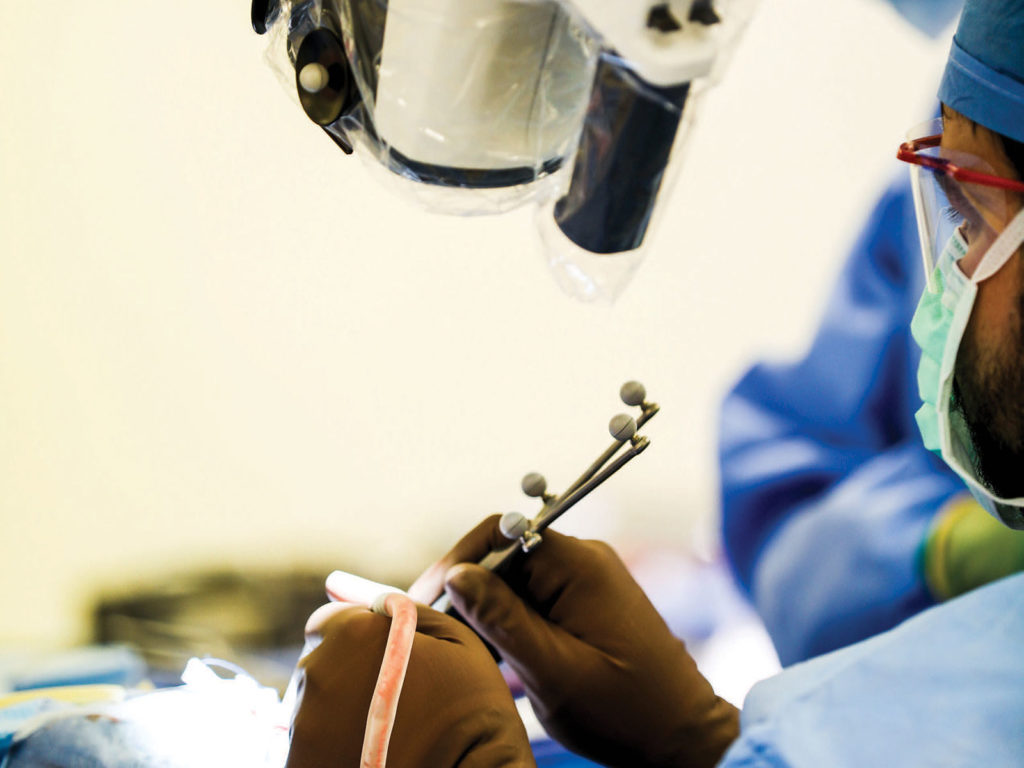
With advances in neuroscience and technology, surgeons and researchers are developing new and improved techniques for performing neurosurgical procedures. By leveraging cutting-edge equipment and imaging techniques, surgeons can gain essential spatial orientation in the operating room. The most notable of these techniques is neuronavigation technology, which includes brain mapping, 3D visualization software, augmented reality computer systems, deep brain stimulation (DBS) technologies, and more.
Brain mapping unlocks the ability to visualize comprehensive 3-dimensional (3D) representations of a patient’s brain. This facilitates specific targeting of neurosurgical treatments in order to minimize predicted effects on healthy tissue while maximizing care outcomes. Moreover, by utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) systems during preoperative planning stages such as image segmentation or tumor resection planning, neurosurgeons can enhance their decision-making process about patient treatment options.
Additionally, advanced imaging tools allow for further refinement when it comes to treatment plans since they offer a detailed view inside sophisticated brain structures that was previously not accessible; allowing for greater accuracy when accessing targeted areas during operations such as tumor resections or implanted DBS electrodes. Furthermore, advancements such as MRI-guided skull tracking increase surgical safety by knowing a patient’s precise location during surgery in order to avoid damaging nearby neural structures or affected tissue areas due to involuntary head movement from the patient under anesthesia.
Conclusion
Overall, Neurosurgery is continuing to see technological advancements that are changing the face of the medical field. Modern motion control technology and new imaging techniques give surgeons greater control over their tools and allow them to reduce risks while increasing accuracy and precision during surgery. This has enabled them to provide better care to their patients, even in the most challenging cases.




