Can You Test Negative for an STD But Still Have One?
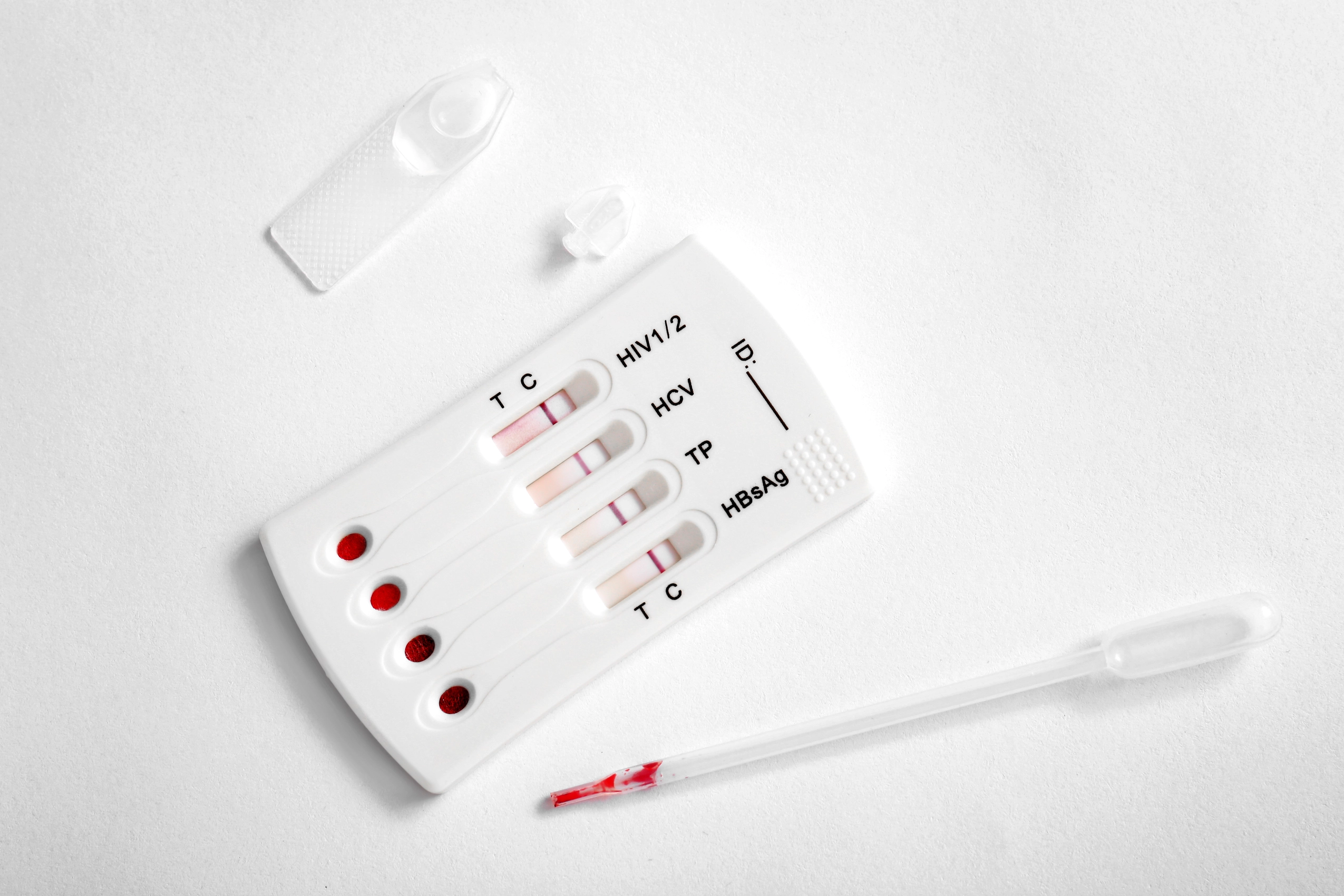
If you’re like most people, you probably think that testing for STDs is a pretty important part of your sexual health. After all, if you don’t know if you’re STD-free, chances are you’re putting yourself at risk. Unfortunately, STD testing isn’t as simple as it seems. In fact, it can be quite complicated and there are a few factors that can complicate the test results. In this blog post, we will explore one such complication—can you test negative for an STD but still have one? We’ll answer this question and more in order to help you make informed decisions about your sexual health.
What is an STD?

There are many sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), but only a few are actually life-threatening. Here’s a look at the top five STD infections and their risks:
- Syphilis. This infection can cause serious health problems, including blindness, deafness, heart problems, and even death. Signs and symptoms of syphilis include a rash on the skin, sores that won’t heal, and pain when urinating or having sex. If you think you may have contracted syphilis, get tested right away!
- Gonorrhea. This STD is easily spread through sexual contact — including vaginal, anal, or oral sex — with someone who is infected. Symptoms of gonorrhea include discharge from the penis or vagina, burning during urination, yellowing of the eyes and skin (jaundice), pain during sexual intercourse, and difficulty breathing.
- Chlamydia. This STD is also easily spread through sexual contact — including vaginal, anal, or oral sex — with someone who is infected. Symptoms of chlamydia include discharge from the penis or vagina, a burning sensation when urinating or during sex (dysuria), feverfew pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), painful intercourse (dyspareunia), and bleeding between periods.
- HPV. This virus is responsible for most cases of cervical cancer, and can also be spread through sexual contact — including vaginal, anal, or oral sex — with someone who is infected. Symptoms of HPV include a persistent sore on the vulva or anus, difficulty wearing a tampon or having an orgasm, abnormal Pap smears, and cancer.
- HIV. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV is easily spread through sexual contact — including vaginal, anal, or oral sex — with someone who is infected. Symptoms of HIV infection include fever, fatigue, weight loss, diarrhea, night sweats, swollen lymph nodes in the neck and chest (median node), and rash.
How are STDs Diagnosed?
There are three primary ways that STDs are diagnosed: through a physical examination by a healthcare professional such as a doctor or nurse, through testing of secretions or blood samples, or through DNA analysis of infected cells. All three methods have strengths and weaknesses.
Physical examination is generally the most accurate way to diagnose an STD, but it is not 100 percent accurate. For example, if someone has swollen lymph nodes in the neck area which are characteristic of HIV infection, then this would be considered a positive diagnosis of HIV even if the person tests negative for HIV antibodies.
Testing of secretions or blood samples can also be very accurate, but it can be difficult to get infected people to provide these samples. DNA analysis of infected cells can be very accurate, but it is expensive and may not be available in all cases.
What are the Symptoms of an STD?

There are many different STDs, and each one can cause different symptoms. Some common symptoms of STDs include:
– A fever
– Swollen glands
– Pain when urinating or having sex
– A rash
Treatment for an STD typically involves antibiotics, and sometimes a prescription medication to treat the symptoms. If you think you may have contracted an STD, it’s important to talk to your doctor about your symptoms. A blood STD test can help determine if you have it.
How Can You Test for an STD?
There are a few ways to test for an STD but the most common is by taking a urine or blood test. If you have any symptoms, such as unusual bleeding, pain during sex, or discharge from the penis, then you should see your doctor for testing.
This testing is important because not all symptoms are always signifiers of an STD. If you have any questions or concerns, talk to your doctor.
How are STDs Treated?
There are a few ways to treat STDs, but all of them involve taking antibiotics. If you think that you may have contracted an STD, you should talk to your doctor. They can test you for the STD and give you the best treatment possible.
Some STDs can be treated with antibiotics. For example, gonorrhea is treated with antibiotics taken orally (by mouth). If you have chlamydia, your doctor will give you a pill to take every day. The pill will treat the infection.
If you don’t want to take any antibiotics, there are other treatments that can be used. For example, condoms can help prevent STD transmission. And if you do get an STD, there are treatments available that will help cure it.
Can You Still Get an STD if You Test Negative for it?
There is no definitive answer to this question since there are a variety of STDs that can be contracted even if you test negative for the virus. It is important to know that some STDs, such as HPV, cannot be detected by a standard blood test and must be detected through other means, like cervical cancer screening. So always consult with your doctor if you have any questions about whether or not you’re at risk for an STD.
Conclusion
If you are sexually active but you are negative for an STD, it is important to talk to your doctor. There could still be something going on that needs to be addressed and tested. Sometimes there can be false negatives due to HPV or other reasons, so it is always a good idea to get checked out by a doctor just in case.




